What Is Hedging?
Hedging is a risk management strategy applied to all financial instruments to offset risks by taking different positions. This way, investors are offsetting risks associated with a single currency by opening additional positions. Moreover, their goal is to protect themselves against adverse moves in markets. Join us in exploring Forex hedging strategies.
How Forex Hedging Works
Investors using hedging in the Forex market are strategically opening multiple positions to protect their capitals against unwanted moves in markets. Hence, they are mitigating risks associated with the currency markets by making sure that their exposure is balanced across the board.
How to Do Forex Hedging
As said earlier, the main aim of Forex hedging is to reduce the overall risk in the portfolio. Given the natural volatility of currency markets, investors are using numerous tools to offset risks.
Let’s use a simple example to show how Forex hedging works in practice. You decided to buy EUR/USD at a market price of $1.10, once the price broke above the key short-term resistance.
The overall bias is now clearly to the upside, hence you are looking to ride the trend as long as possible. The price action then hits critical mid-term resistance at $1.1420. At this point, you realize that there is a realistic chance the market moves in the opposite direction.
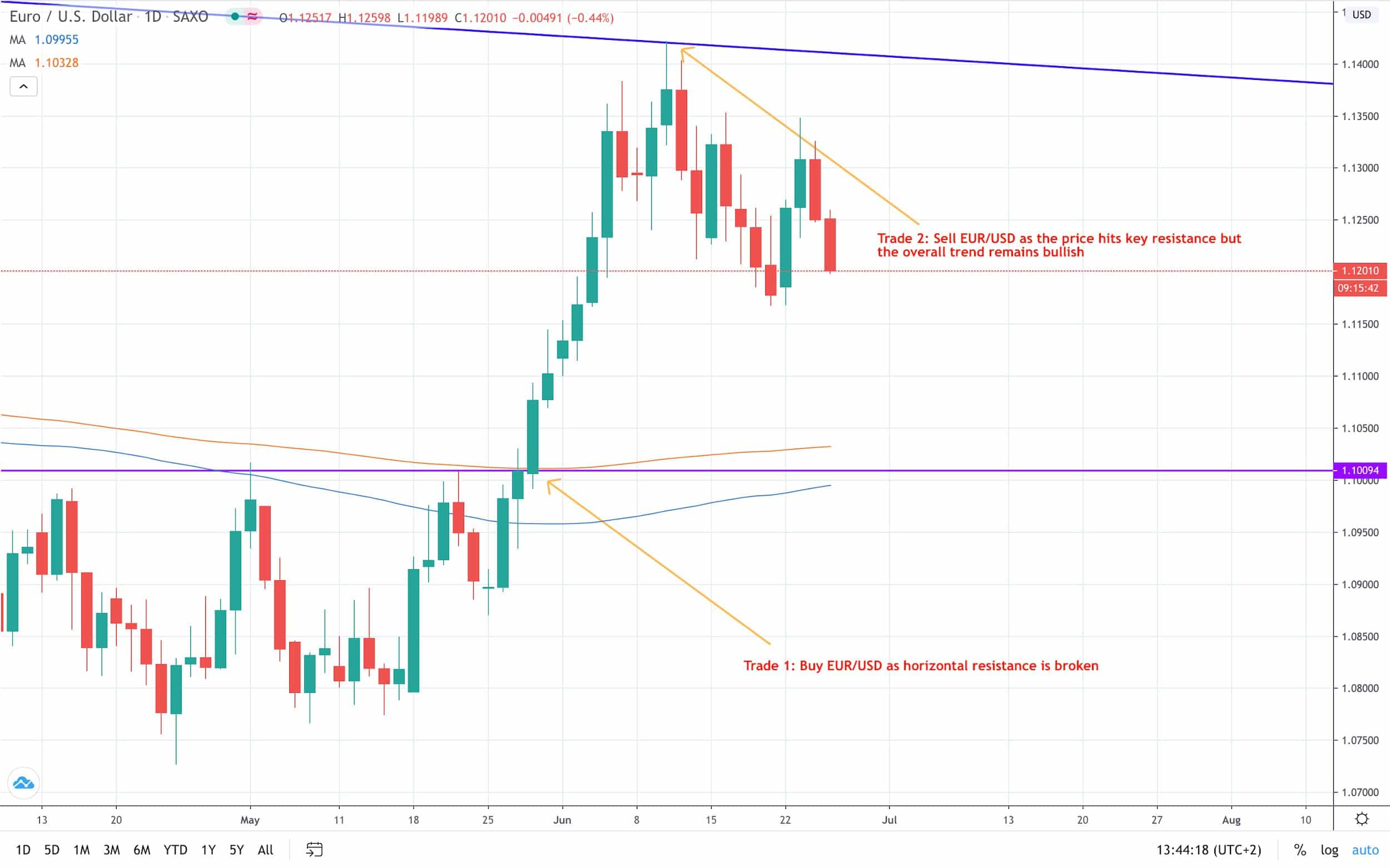
Since you still believe that the overall trend is bullish and EUR/USD has more room for gains, you decide against booking profits. Instead, you ultimately decide to open a second trade to hedge. This way, you are protected against the short-term losses in your first trade. The second one is a short-term trade of a swing nature.
If the pair continues higher and breaks above the resistance, your first trade will extend gains, while the new trade will result in losses. However, if the pullback from $1.1420 takes place, gains in the second trade will help you offset losses from the first trade.
Forex Hedging Strategies
The example that we described above is one of the basic Forex hedging strategies. By opening the opposite trade in EUR/USD, we protected our original position from the pullback. This is why this type of mitigating risk is called direct hedging.
In reality, there are numerous different trading strategies that are designed around hedging in Forex. Here, we will describe two popular Forex hedging strategies.
Direct hedging
Direct hedging can take different forms. We can, as shown above, decide to hedge while our trade is in the green. One of the other forms, as described below, is focused on buying us time until our trade shifts from red to green.
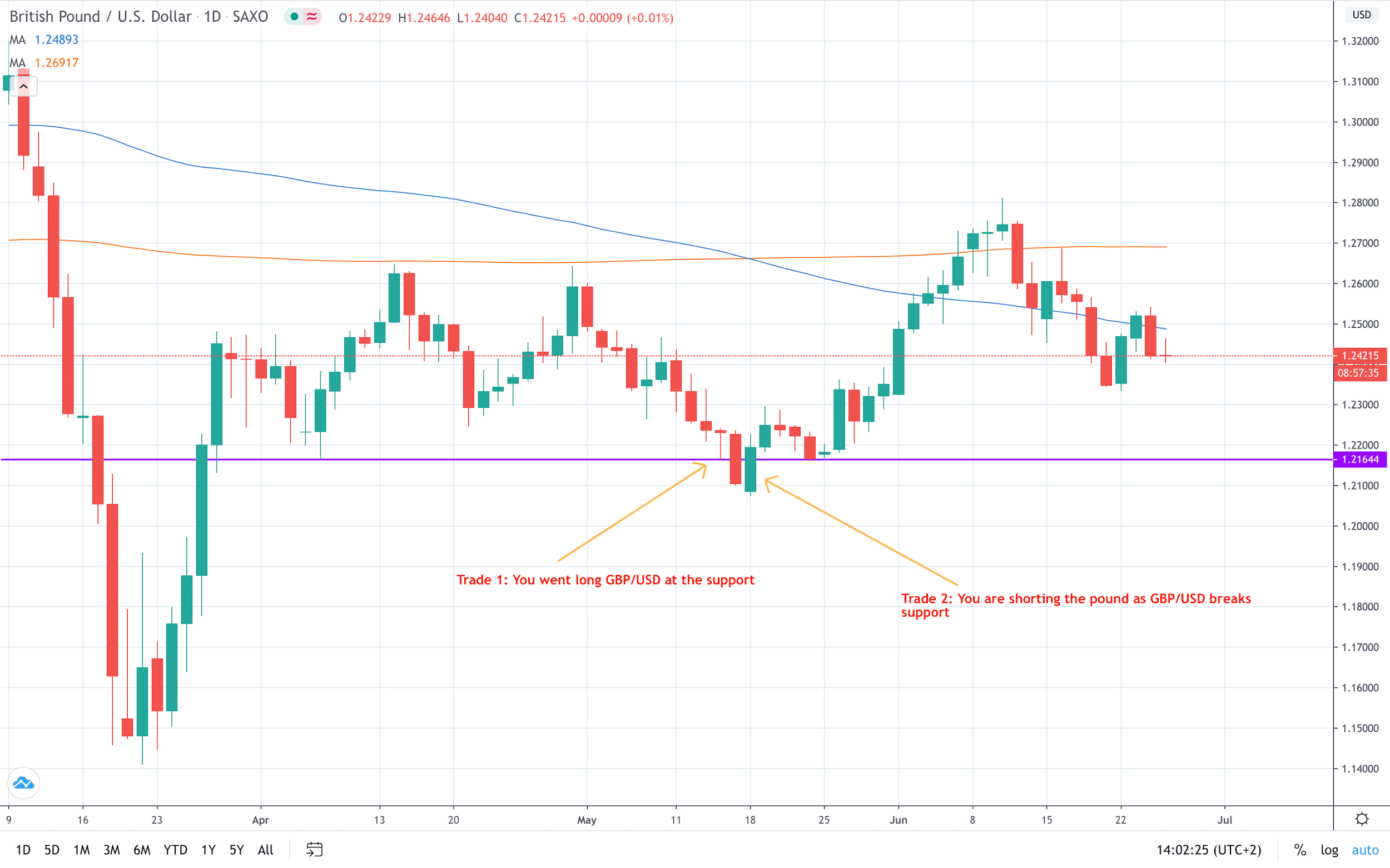
You decided to take a long position in GBP/USD near the horizontal support at $1.2165. Secondly, the price action then breaks below, threatening to increase your losses. In order to mitigate risk from this happening, you decide to take a short position in GBP/USD.
Your actions are based on the belief that the downturn is temporary and the overall bias is still to the upside. Hence, you decide the second trade is buying you time. If you didn’t hedge against the original position, closing your trade means you are accepting a loss.
This way, you hope that the trend reversal will take place soon. If the downturn is indeed temporary, you will make money with the second trade before the original one shifts to the green.
Some brokers, mainly in the United States, don’t allow direct hedging. Hence, you may have to do a bit of research and find brokers that allow direct Forex hedging.
Hedging with multiple currencies
Another form of hedging in Forex involves taking opposite positions in pairs that are correlated. Let’s use an example again to demonstrate how this strategy works in practice.
Initially, you went long EUR/USD before deciding to hedge your USD exposure by buying the dollar against other currency e.g. GBP/USD. Therefore, you are going long EUR/USD and taking a short position in GBP/USD.
If the former falls, you will record losses, however, these are likely to be mitigated by gains in the latter, and vice versa. Remember, Forex hedging is more focused on mitigating risks than making profits in trades with high risks.
While direct hedging is pretty straightforward, hedging more than one currency pair is recommended for more advanced Forex traders. In our case, besides mitigating risks in the USD, you are also exposed to EUR and GBP.
Eventually, one of the scenarios may be that you lose, or gain, money on both trades. Or, in most cases, you’d hope that one position might generate more profit than losses occurred in the other position.
Summary
Forex hedging is all about mitigating risks. Investors use this trading strategy to protect their capitals against adverse moves in the currency markets. While there are different forms of Forex hedging, direct hedging is arguably the simplest and most popular format of mitigating risks by taking multiple positions.
PEOPLE WHO READ THIS ALSO VIEWED: